Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid Plant (EDTA)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a chelator of metal ions. It is a substituted diamine, which has antibacterial activity. EDTA removes the undesirable effects of ferric, cupric and manganic ions in bleaching. It prevents cellular division, chlorophyll synthesis and algal biomass production. EDTA is an inhibitor of metalloprotease. It has anticoagulant property.
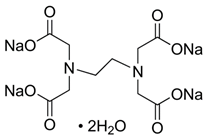
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) Molecular Weight 416.2, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the Linear Formula (NaOOCCH2)2NCH2CH2N(CH2COONa)2•2H2O This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron and calcium ions. It binds these ions as a hexadentate (Six-toothed) chelating agent. EDTA is produced as several salts, notably disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA.
EDTA and its sodium products have a wide range of applications, with global annual consumption exceeding 100,000 tons.
The major applications as follows:
1) Pulp and paper industry: Machine pulp bleaching, chemical pulp, de-inking, scale inhibition for digester/evaporator, stabilizer in hydrogen peroxide transportation; EDTA inhibits the ability of metal ions, especially Mn2+, from catalysing the disproportionation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used in chlorine-free bleaching.
2) Water treatment: Boiler, cooling water system, evaporator, heat ex-changer; for the dissolution of scale in boilers both rely on EDTA and related complexants to bind Ca2+, Mg2+, as well as other metal ions. Once bound to EDTA, these metal centres tend not to form precipitates or to interfere with the action of the soaps and detergents. For similar reasons, cleaning solutions often contain EDTA.
3) Industrial/scientific research as cleaning agent: Laundry detergent to reduction of water hardness in laundry applications; building cleaning, disinfectant, milk/beverage/food processing plant cleaning, car cleaning agent, hand sanitizer;
4) Photographic industry: Developer, bleach;
5) Agriculture: Micronutrients, herbicides;
6) Textile industry: Printing and dyeing, bleaching, washing, desizing; it prevents metal ion impurities from modifying colours of dyed products.
7) Food processing industry: De-colorization, taste remove; In soft drinks containing ascorbic acid and sodium benzoate, EDTA mitigates formation of benzene (a carcinogen). EDTA also added to some food as a preservative or stabiliser to prevent catalytic oxidative decolouration, which is catalysed by metal ions.
8) Cosmetics industry: In shampoos, cleaners, and other personal care products, EDTA salts are used as a sequestering agent to improve their stability in air.
9) Medicine: Lead poisoning treatment, anemia treatment, quaternary ammonium salt, antibiotics, eye care products, mildew preparation, drug stabilization, mineral supplements;
10) Metal treatment: Metal cleaning, steel processing, coating, plating, metal final treatment, mainly used to sequester metal ions in aqueous solution.
11) Cement blending: EDTA is used in the cement industry for the determination of free lime and free magnesia in cement and clinkers.
12) Rubber/polymer processing: styrene butadiene adhesive, PVC, polymerization system stabilizer;
13) Laboratory applications: In the laboratory, EDTA is widely used for scavenging metal ions, its commonly used in biological and electrophoresis buffer systems as a chelator of divalent cations. Some proteolytic enzymes and nucleases require divalent cations for activity. The addition of EDTA reduces the chance of sample degradation.
14) Others: Gas washing, oil field production, chemical production, leather tanning, mineral processing…
EDTA PLANT BY OUR ADVANCED TECHNOLOGIES
There are four types of technologies available with Synopsis Chemitech: Chloroacetic Acid Method; Hydrocyanic Acid Method; Hydroxy acetonitrile Method; and Sodium Cyanide Method. Each process has different advantages.
- Chloroacetic Acid Method;
Chloroacetic acid reacts with sodium carbonate to produce sodium chloroacetate, which is condensed with ethylenediamine in alkaline solution to form the EDTA sodium salt, after that its neutralized with sulfuric acid to obtain the products of EDTA. Although this method avoids the use of cyanide, but the disadvantage is there are too much steps of the reaction with the long process times, also when the chloroacetic acid reacts with sodium carbonate it will easily generate sodium glycolacetate, this then results in low yield of the products. Also, due to the formation of large amount of sodium chloride, chloride ion in the product is easy to exceed the standard, so that the product quality may not stable. In addition, this method has higher energy consumption, high investment on the equipment / devices and high production cost, so the market competitiveness at lower side, at present, this process has been eliminated from industry.
- Hydrocyanic Acid Method;
This method used the liquid hydrocyanic acid, formaldehyde and ethylenediamine as raw materials, reacting under acidic conditions to produce ethylenediamine tetraacetonitrile, and then through the hydrolysis with caustic soda and acidification via sulfuric acid to obtain the EDTA. the product obtained by this method has a good quality, but the yield of the products at lower side, the production cost too high, the most important is that the main raw material ‘liquid hydrocyanic acid’ as an extremely dangerous chemical are too challenged for the storage and transportation, it is not suitable for industrialized production, therefore the market competitiveness too low.
- Sodium Cyanide Method
Liquid sodium cyanide, formaldehyde and ethylenediamine are used as raw materials to produce EDTA sodium salt, and EDTA sodium salt will acidified with sulfuric acid to obtain EDTA products. However, the sodium cyanide as an extremely toxic hazardous chemical is strictly controlled by law. There are special regulations for the production, storage, and transportation as well as location selection, environmental protection and safety management, so the entry threshold for such plant will be higher than others.
- Hydroxy acetonitrile Method
Hydroxy acetonitrile reacted with ethylenediamine and sodium hydroxide as raw materials to produce EDTA sodium salt, afterwards acidified with sulfuric acid to produce the EDTA products. Hydroxy acetonitrile used in this method is generated from hydrocyanic acid and formaldehyde (provide by SC), so it can easily be used to remove the carbon dioxide in the hydrocyanic acid synthesized by Anscher method and reduce the consumption of caustic soda. Moreover, this method adopts single material flow addition in the synthesis of tetrasodium salt, which is more convenient for the production control compared to the double material flow addition of sodium cyanide method. At the same time, due to the nature of hydroxyl acetonitrile excessively active, it may cause to generate the organic by-products at higher side with large amount of waste water, difficult to recycle and treat the sodium sulfate as a by-product.
We recommend our client based on Hydroxy acetonitrile Method for their EDTA plant, SC has modified and improved the hydroxy acetonitrile method of cleaning process for the production of EDTA, through our optimized process reduce the material consumption, solved the problem of by-product sodium sulfate recycle process and based on the design of “zero emissions”; clean production with good environmental protection. The output rate of production and raw materials / power consumption are better than others.
Main Raw Material for EDTA Production
The major raw materials for EDTA production are Hydroxy acetonitrile; Ethylenediamine; Sodium hydroxide; Sulfuric acid; and Caustic soda flake; and the by-product from the process will be Sodium sulfate and Ammonium sulfate. Due to the issue of the operation costs and safety purchase the Hydroxy acetonitrile and Ethylenediamine may too challenge to client, therefor, Synopsis Chemitech will propose client to build the Hydroxy acetonitrile plant and Ethylenediamine plant as a composition of the EDTA plant. The main technologies of Hydroxy acetonitrile plant and Ethylenediamine plant are as below;
Technology of Hydroxy Acetonitrile Plant
Hydrocyanic acid method will be the main process for the Hydroxy acetonitrile production now, under normal pressure, hydrocyanic acid reacts with water solution of formaldehyde under a certain temperature to generate hydroxyl acetonitrile directly, at same time it will release a large amount of heat. the reaction equation is as follows:
HCN + HCHO → HOCH2CN
Hydrocyanic acid is highly toxic, gaseous at room temperature (Boiling point 26°C) with active nature, storage not recommended generally, It shall be immediate production and demand or converted it into stable cyanide (such as sodium cyanide) for use. the main production methods include ammonia oxidation method; light oil cracking method; acrylonitrile by-product method, etc.
……
……
For more information, please send email to info@synopsischemitech.com
Technology of Ethylenediamine Plant
The main mature technology for Ethylenediamine production has two options which are Alcoholamine Ammoniation process and Dichloroethane Ammoniation process. The other methods have not yet been industrialized due to the source of raw materials and high production cost. Dichloroethane ammoniation method uses polyethylene polyamine as the main by-products, while ethanolamine ammoniation method uses piperazine and its derivatives as the main by-products.
……
……
For more information, please send email to info@synopsischemitech.com





